Simple Deployment
Introduction
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform used for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It provides a way to orchestrate containers, automating tasks such as deployment, scheduling, load balancing, and fault recovery, making containerized applications run efficiently in a distributed system.
Advantages of Kubernetes include:
- Automation: Kubernetes automates tasks such as deployment, scheduling, load balancing, and fault recovery, reducing the amount of manual work required.
- Scalability: Kubernetes can manage thousands of containerized applications in large-scale clusters, with good horizontal and vertical scalability.
- Flexibility: Kubernetes supports multiple container runtimes and multiple cloud platforms, allowing applications to be deployed and managed in different environments.
- Reliability: Kubernetes provides powerful fault recovery mechanisms and self-healing capabilities, ensuring high availability and reliability of applications.
- Community support: Kubernetes is an active open-source project with a large community support and ecosystem, allowing for quick updates and support.
Quick Start
If you want to deploy the Tailchat project on Kubernetes, you can find the prepared simple Tailchat deployment configuration in the docker/simple/k8s subdirectory of the project directory. These configuration files include Kubernetes resource definitions for running Tailchat, such as StatefulSet, Service, and dependencies such as databases and persistent storage. These resource definitions allow you to quickly deploy a simple Tailchat project on Kubernetes without manually creating and configuring these resources.
Note that the deployed Tailchat in this tutorial does not include the complete Tailchat ecosystem, such as the Open Platform and Admin Management Platform.
Environment Dependencies
To start this chapter, we assume that you have a working Kubernetes environment ready. This section does not describe how to set up a k8s environment.
Getting Started
First, we need to clone the project repository:
git clone git@github.com:msgbyte/tailchat.git
Change the working directory to the configuration file directory:
cd docker/simple/k8s
At this point, you can see many prepared configuration files, and we can start by running a single command:
kubectl apply -f namespace.yml -f pv.yml -f mongo.yml -f minio.yml -f redis.yml -f tailchat.yml
This command will create the namespace, create pv and pvc, create mongodb, minio, redis, and other necessary third-party middleware, and finally start a multi-instance tailchat service.
You can check the status of each service using the following command:
kubectl get svc -n tailchat
Routing and Load Balancing
When all services are ready, our Tailchat service is now running in the cluster, but we cannot access it because it has not been exposed to the outside.
For local testing, we can use the port forward function to map the port of a pod to the local machine. In a production environment, however, we need to build routing and forwarding.
Taking traefik as an example:
Traefik is an open-source reverse proxy and load balancer designed specifically for routing and load balancing traffic in containerized applications and microservices architectures. Traefik supports multiple backend services, including Docker, Kubernetes, Mesos, Swarm, Consul, Etcd, and more. It can automatically discover and configure backend services and route traffic to the corresponding service instances based on rules.
Installing Helm and Adding Repository Address
The installation of helm is not discussed here. We execute the following command to add traefik to the repository list:
helm repo add traefik https://helm.traefik.io/traefik
Installing Traefik in the Tailchat Namespace
helm install traefik traefik/traefik -n tailchat
Starting Ingress Resource Declaration
kubectl apply -f ingress.yml
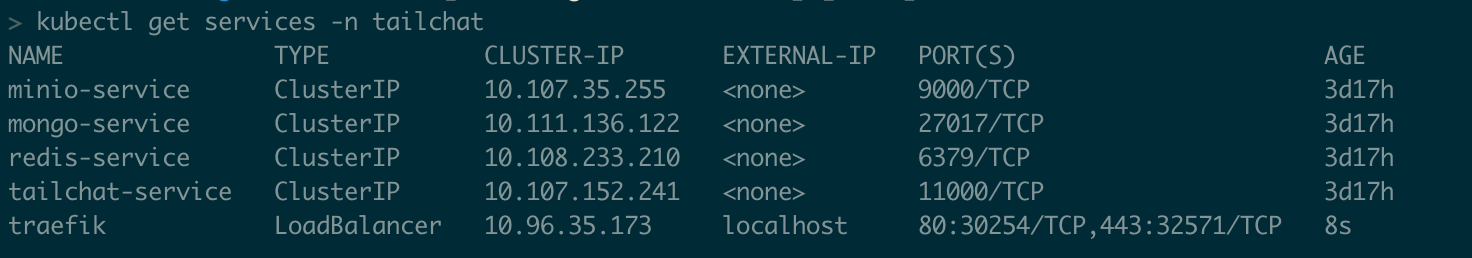
If everything is ok, you can see the following output using the following command:
kubectl get services -n tailchat
Setting up DNS Services
You can modify the domain address configuration in the ingress.yml mentioned above, which defaults to http://tailchat.internal.com/.
If you do not wish to modify or do not have a domain name, you can modify the hosts file to achieve this:
sudo vim /etc/hosts
Then add the following path:
127.0.0.1 tailchat.internal.com
Now you can open your browser and visit http://tailchat.internal.com to access the Tailchat service deployed on Kubernetes.
Of course, you can also check the availability of the service by visiting the following address:
http://tailchat.internal.com/health